Unsere vernetzte Welt verstehen

Wie „Leave” Twitter erobert hat: Eine Analyse von 7,5 Millionen Brexit-Tweets
Wie verhielten sich Twitter Nutzer während der Brexit Kampagne, und besteht ein Zusammenhang zwischen sozialen Medien und Wahlverhalten? HIIG Gastforscher Max Hänska sammelte zusammen mit Stefan Bauchowitz über 7.5 Millionen Tweets zum Thema Brexit in den Wochen vor dem Referendum und stelle fest, dass Befürworter des EU-Austritts in größeren Zahlen und mit größerer Intensität auf Twitter aktiv waren. Twitteraktivität korrelierte mit dem Wahlverhalten: in den Regionen, die für den Austritt aus der EU stimmten, überwog auch die Anzahl euroskeptischer Nutzer des Dienstes.
How did Eurosceptic (leave) and pro-European (remain) activity compare on social media in the run-up to the EU referendum, and was there a relationship between social media users and votes? To find out how leave and remain compared, we collected more than 7.5 million Brexit related tweets during the 23 days leading up to the referendum through Twitter’s streaming API. We used a support vector machine to identify which tweets clearly supported the leave or remain camp (and manually coded a random sub-sample of those tweets to ensure our allocation was reliable). Due to the polarizing nature of the issue, the process worked well, and the model correctly identified most tweets. We used the result of this exercise to assign each user in our sample to one of the two camps.
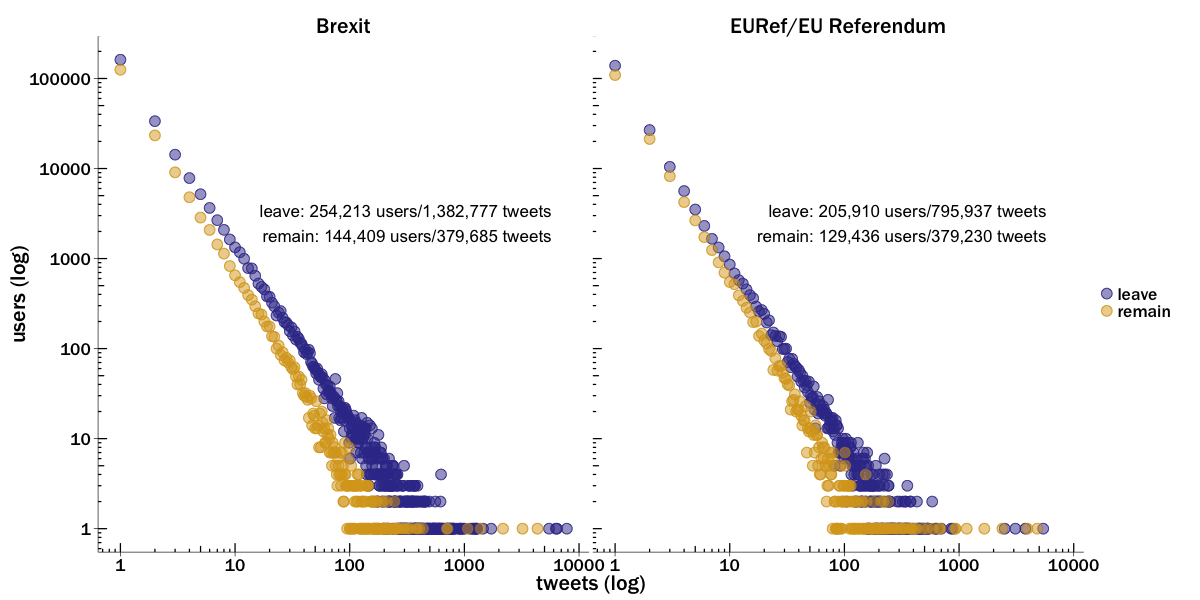
We collected tweets containing the terms Brexit, EUref and EU Referendum, all of which were frequently used to refer to the referendum. While the term Brexit has great currency across both camps, it was used more often by users who wanted to leave the EU as it lends itself more easily to positive slogans, e.g. “Can’t wait for #Brexit to win!” or “Brexit to save Europe” and “Brexit means Brexit”. Even though EURef and EU Referendum are more neutral terms, in both sub-samples we found that support for leaving, measured by the number of tweets, outstripped support for remaining by a factor of 2.3 and 1.75 respectively. The margins confirm a slight bias in the term Brexit, where the strength of leave over remain was more pronounced. Overall it is clear that the army of leave users was larger in number and more active in tweeting their cause (see Figure 1).
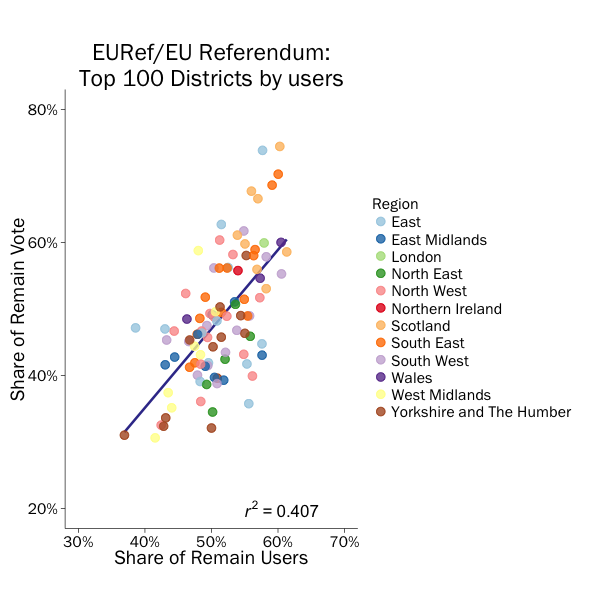
Other researchers examining Google search trends, Instagram posts, and Facebook found something similar – i.e. that Eurosceptic views were being communicated with greater intensity by a greater number of users. Researchers from Loughborough University revealed that, weighted for circulation, 82% of newspaper articles were pro-Leave (Loughborough University, 2016). British people had greater exposure to Eurosceptic than pro-European opinions in both print and social media. We also mapped Twitter activity onto local authority districts. To do this, we used Google’s and Bing’s geo coding services to translate user-provided location information into geographical coordinates, which we then matched with local authority districts. This is not an exact science, both because many users provide no or fictitious location information in their profiles, and because the more granular the geo-location information required, the more error-prone the result. As many users specify their location as London rather than its constituent boroughs, we aggregated all tweets from users located there. We plotted the share of users supporting remain against share of the remain vote. We excluded districts where we identified fewer than 200 users, giving us usable data for 100 local authorities.
There is clearly a pattern in how the referendum campaign unfolded on Twitter, with those wanting to leave communicating in greater numbers and with a greater intensity. Districts with a greater share of Twitter users supporting leave also tended to vote for leaving the EU, meaning that Twitter activity correlates with voting in the referendum. Yet we must be cautious to avoid over-interpretation. This particularly applies to claims that social media can predict election outcomes, the problems of which have been pointedly enumerated. Finding a pattern in the data post hoc is quite a different thing than confidently identifying and interpreting the pattern ex ante – the leave camp was ahead on social media by a much larger margin than it ultimately was in the vote. This means it is unclear how researchers could have interpreted the results of a Twitter analysis before the vote. The most significant problem is that we lack the demographic descriptors of social media users that would enable us to weight or interpret results.
Nevertheless, given that Twitter users are generally thought to be younger and young people tended to vote remain, the result is surprising either way. It seems plausible that leave voters were more motivated, and consequently more active on Twitter. It also seems likely that slogans such as vote leave, take control, or even Brexit lent themselves better to a simple message (this is particularly useful given the constraints of a tweet), and allowed different interpretations, with the result that users could project their desired meaning onto the slogan. Whether in the press or on social media, British voters were more likely to encounter messages that favoured leaving the EU than those that favoured remaining.
This blogpost was first published on the Brexit blog by London School of Economics. Stefan Bauchowitz holds a PhD from the London School of Economics. Max Hänska is a lecturer (Assistant Prof.) at De Montfort University (UK) where his research interests center on social media, political communication and collective decision-making. During the summer he was a visiting researcher at HIIG.
References
Loughborough University (2016). 82% circulation advantage in favour of Brexit as The Sun declares.
Dieser Beitrag spiegelt die Meinung der Autorinnen und Autoren und weder notwendigerweise noch ausschließlich die Meinung des Institutes wider. Für mehr Informationen zu den Inhalten dieser Beiträge und den assoziierten Forschungsprojekten kontaktieren Sie bitte info@hiig.de

Jetzt anmelden und die neuesten Blogartikel einmal im Monat per Newsletter erhalten.
Offene Hochschulbildung
Freundlich, aber distanziert: Die unbeabsichtigten Folgen KI-generierter E-Mails
KI-generierte E-Mails sparen Mitarbeitenden Zeit und erleichtern den Arbeitsalltag. Aber verlieren wir dadurch unsere Kommunikationsfähigkeiten?
KI am Mikrofon: Die Stimme der Zukunft?
Von synthetischen Stimmen bis hin zu automatisch erstellten Podcast-Folgen – KI am Mikrofon revolutioniert die Produktion digitaler Audioinhalte.
Haben Community Notes eine Parteipräferenz?
Dieser Artikel analysiert, ob Community Notes Desinformation eindämmen oder ob ihre Verteilung und Bewertung politische Tendenzen widerspiegeln.