Making sense of our connected world

The AI Transparency Cycle
Why AI transparency?
AI is omnipresent and invisible at the same time. Do you notice every time you interact with an algorithm? What data is being collected and processed while you casually scroll through social media or browse products on retail websites? Privacy statements by platform providers promise full transparency, but what does this even mean and what is the underlying goal?
The devil’s in the details
Defining transparency has never been straightforward and defining transparency in the context of AI systems is no exception to that. Transparency, in a broad sense, is what one can perceive, comprehend and lets one act in light of that knowledge. Considering big tech companies’ privacy statements spanning well beyond 10.000 words, aiming to inform users about their intentions and protective rights, the effectiveness of transparency measures in place appear questionable. Do you understand, for example, when you interact with an AI system and why platforms recommend certain content to you? Even if this information might be available it might not be transparent, since availability does not always equal attainability.
Metaphors of transparency
Research on the use of the metaphor transparency (Ball, 2009) reveals from the context of non-governmental-organisations and other political stakeholders, that by transparency we imply different ends of information sharing. Ball (2009) identified three: accountability, openness and efficiency. Openness is probably the most intuitive goal of transparency. Openness enforces transparency to create trust. For instance, it creates trust by allowing viewers to see what is protected from others, e.g. to protect one’s privacy. This includes not only informed decision-making, but also knowing which questions to ask in the first place. Efficiency might be less intuitive as a goal of transparency, but it’s none the less crucial for today’s complex societies. Only by knowing and understanding complex systems can we allow them to function efficiently, since we do not need to question their workings each time we depend on them. Therefore, transparency is also important for progress in societies. Last, but not least, let’s look closely at accountability.
Accountability
The third important goal of transparency often recognized is accountability. Regarding AI systems, this refers to the question of who is responsible for each step in the development and application of machine learning algorithms. Mark Bovens, who researches public accountability, defined it “as a social relationship in which an actor feels an obligation to explain and to justify his or her conduct to some significant other.” (Bovens, 2005). He sees five characteristics for public accountability, namely 1. public access to accountability, 2. proactive explanation and justification of the actions, 3. addressing a specific audience, 4. an intrinsic motivation for accountability (in contrast to action only on demand), and 5. the possibility of debate, including potential sanctions in contrast to unsolicited monologues. Especially characteristic four presents a challenge, considering the common perception of accountability as a tool for preventing blame and legal ramifications. For accountability to be realised, practising diligent AI transparency is crucial, so it does not turn “into a garbage can filled with good intentions, loosely defined concepts, and vague images of good governance.” (Bovens, 2005).
One-size-does-not-fit-all
Transparency is a constant process – not an everlasting fact. It is to be viewed in its context and the perspective of stakeholders affected (Lee & Boynton, 2017). A large company providing transparency regarding its software to a governmental agency cannot give the same explanation and information to a user and expect transparency to be achieved. In a way, more transparency can lead to less transparency through the overwhelming quantity of information provided to the wrong recipient. Relevant factors to tailor AI transparency measures include the necessary degree of transparency, the political or societal function of the system, target group(s) and specific function of transparency. At the core of it lies the need for informed decision-making.
AI Transparency is a Multi-Stakeholder Effort
In practice, transparency cannot be implemented by a single actor, but has to be applied in every step of the process. A data scientist is often not aware of ethical and legal risks; and a legal counsel, for example, cannot spot those by reading through code. This becomes especially apparent in the case of unintended outcomes, calling for not only prior certifications, but also periodic auditing and possibilities of intervention for stakeholders at the end of the line. A frequent hurdle for clearer transparency standards in this area arises from the conflict between the protection of business secrets and the necessity to get access to software codes for reasons of auditing.
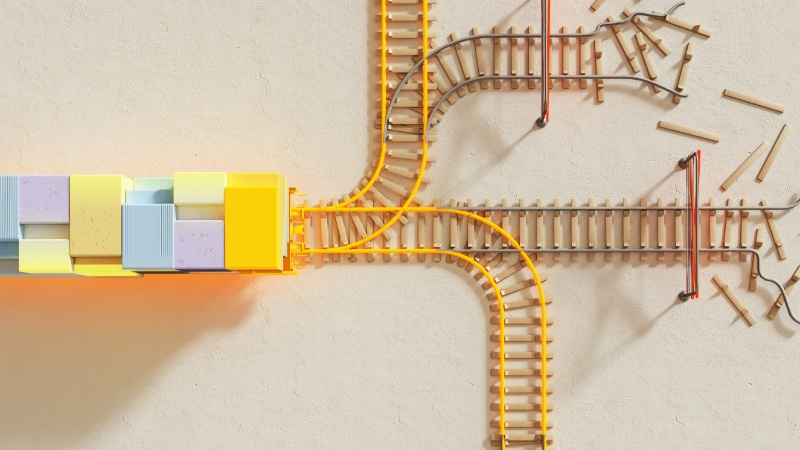
The ‘AI Transparency-Cycle’ (see graphic above) provides an overview on how the many dimensions of AI development and deployment and its ever-changing nature could be modelized and serves as a roadmap to solve the transparency conundrum. It is important not to interpret the cycle as a chronological step-by-step manual, but rather as a continuous, self-improving feedback process where development, validation, interventions, and education by the actors involved happen in parallel.
References
Ball, C. (2009). What is Transparency?. Public Integrity, 11, 293-308.
This post represents the view of the author and does not necessarily represent the view of the institute itself. For more information about the topics of these articles and associated research projects, please contact info@hiig.de.

You will receive our latest blog articles once a month in a newsletter.
Artificial intelligence and society
Polished yet impersonal: The unintended consequences of writing your emails with AI
AI-written emails can save workers time and improve clarity – but are we losing connection, nuance, and communication skills in the process?
AI at the microphone: The voice of the future?
From synthesising voices and generating entire episodes, AI is transforming digital audio. Explore the opportunities and challenges of AI at the microphone.
Do Community Notes have a party preference?
This article explores whether Community Notes effectively combat disinformation or mirror political biases, analysing distribution and rating patterns.