Unsere vernetzte Welt verstehen

Links liegen gelassen: Wissenschaftliche Akteure in der Energiewende
Die Energiewende ist vieles: ambitioniert, komplex und hoch politisch. Umso wichtiger erscheint eine enge Verzahnung von Politik, Wissenschaft, Wirtschaft und Zivilgesellschaft. Dies findet im Internet jedoch kaum statt, wie Markus Rhomberg, Axel Maireder, Stephan Schlögl und Jonas Kaiser, assoziierter Forscher am HIIG, in ihrer Studie zeigen. So reicht der Horizont politischer Parteien nicht über Parteigrenzen hinaus und wissenschaftliche Akteure werden im Online-Diskurs zur Energiewende gleich ganz links liegen gelassen.
The German Energiewende is both: a wonderful example for the German tradition of composite words as it combines energy and transition and, thus, a practical description of the ambitious political and social aim to transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources. However, such an ambitious project can only be realized when all societal actors – political, civil society, economics, science, etc. – are at least to some extent on the same page due to the many challenges ranging from national to transnational politics and technical feasibilities to economic liabilities. Political actors thus have to juggle all these interests and also give the actors the feeling that they’re being heard. The attempt to integrate different perspectives, then, should also be visible online, as my colleagues Markus Rhomberg, Axel Maireder, Stephan Schlögl and I assumed.
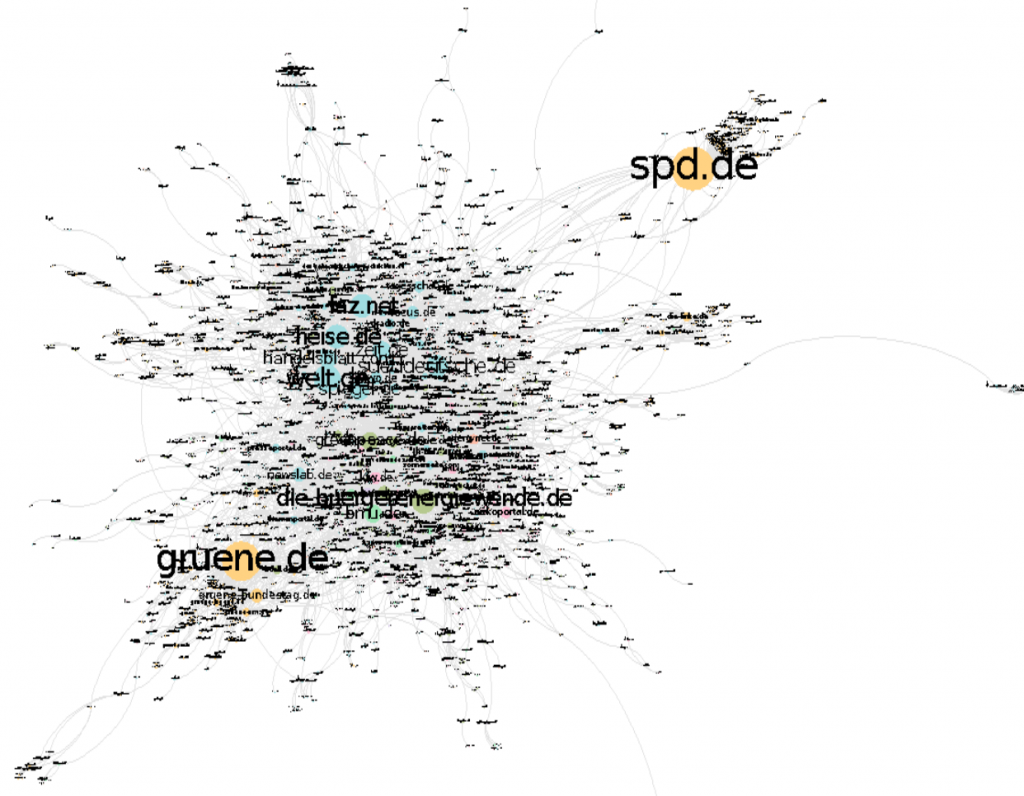
To understand how political actors use the internet to connect with other societal actors, we conducted a hyperlink network analysis of the Energiewende discourse (see the full paper here for free). The data was collected during the 30 weeks before the German federal elections in 2013 where the Energiewende was a prominent topic in the public discourse. Whereas hyperlink analysis usually make use of webcrawlers which consider all links on a site but do not differentiate between relevant and irrelevant links (e.g. blogspam, off-/on-topic, etc.) we used Google’s search engine and only included links between websites that actually mentioned one of our search terms (e.g. Energiewende or EEG) in our sample. The resulting network (see Figure 1) thus truly represents the Energiewende issue network.
In our analysis we found that political actors rarely linked to other actors and mostly linked within their party communities. Indeed, political actors neither prominently linked outside their communities nor were linked to by other actors. The Energiewende network in itself was rather fragmented and was only kept together by actors from the mass media and civil society. Especially the media outlets were very active when it came to linking to other societal fields like economics, science, special interest groups or public administration. So if you are a Luhmann enthusiast this result might not be a shock as it could easily be explained with the mass media’s task to observe other fields, erm, systems and report about them.
One specific aspect which we were only able to mention briefly in our paper, however, was the role of science. The Energiewende is for a myriad of reasons a highly interesting and relevant field for researchers from all different kinds of disciplines. Engineers are looking for ways to make renewable energy sources more efficient, climate scientists are trying to understand the influence the Energiewende will have on Germany’s climate models, economists attempt to calculate the Energiewende’s impact on the GDP and different industry sectors, architects try to build and design more energy friendly houses, etc. In sum, scientists and their results are valuable resources for society in general and political actors in particular.
And yet, scientific actors received little to no attention in our network. Indeed, if links from scientific (n=39) and media (n=76) actors were left out there would have been only 49 links to scientific websites in the span of 30 weeks – and only one from a political actor. But science itself isn’t any better: we only found 74 links to non-scientific websites. Actors from the mass media were the most prominent link targets (22 links), but scientific actors seem to be as uninterested in politics as politics is in science (1 link). To put it bluntly: scientific actors neither linked to other sites nor are linked to by other actors prominently.
Is this just the result of the – perhaps fitting – stereotype of internet avoiding researchers that just do not link much (see also Benedikt’s and my hyperlink analysis of the German academic blogosphere) and who might not even get the internet in combination with academic results that suggest that a high number of outgoing links will also result in more incoming links? Or is this rather a highly alarming finding that suggests that even though scientists are actively involved in the Energiewende discourse – a discourse, mind you, that needs unbiased knowledge and facts as mediators between arguing factions – they are mostly ignored in favor of party lines and lobbying by special interest groups? Or am I biased and think too highly of science’s importance for society and the public discourse?
Perhaps it’s a mixture of all options but one thing is clear: science is talking – but nobody is listening.
This blog post is based on the peer-reviewed article “Energiewende’s Lone Warriors: A Hyperlink Network Analysis of the German Energy Transition Discourse” by Jonas Kaiser, Markus Rhomberg, Axel Maireder, and Stephan Schlögl which was published in the special issue Political Agency in the Digital Age: Media, Participation and Democracy in the open access journal Media and Communication.
Dieser Beitrag spiegelt die Meinung der Autor*innen und weder notwendigerweise noch ausschließlich die Meinung des Institutes wider. Für mehr Informationen zu den Inhalten dieser Beiträge und den assoziierten Forschungsprojekten kontaktieren Sie bitte info@hiig.de

Jetzt anmelden und die neuesten Blogartikel einmal im Monat per Newsletter erhalten.
Plattform Governance
Der Human in the Loop bei der automatisierten Kreditvergabe – Menschliche Expertise für größere Fairness
Wie fair sind automatisierte Kreditentscheidungen? Wann ist menschliche Expertise unverzichtbar?
Gründen mit Wirkung: Für digitale Unternehmer*innen, die Gesellschaft positiv gestalten wollen
Impact Entrepreneurship braucht mehr als Technologie. Wie entwickeln wir digitale Lösungen mit Wirkung?
Bias erkennen, Verantwortung übernehmen: Kritische Perspektiven auf KI und Datenqualität in der Hochschulbildung
KI verändert Hochschule. Der Artikel erklärt, wie Bias entsteht und warum es eine kritische Haltung braucht.